 Are you curious if automated brain lesion segmentation tools can be both highly accurate and reproducible? To confirm this possibility, we compared our fully automated LesionQuant module against manual expert segmentation.
Are you curious if automated brain lesion segmentation tools can be both highly accurate and reproducible? To confirm this possibility, we compared our fully automated LesionQuant module against manual expert segmentation.
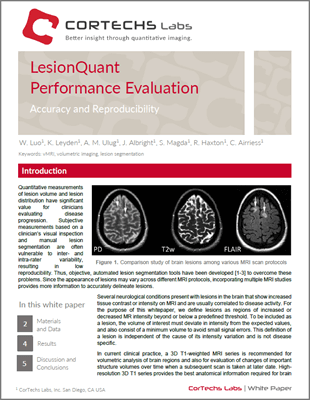
Volumetric brain imaging is a powerful tool for providing clinicians with in vivo quantitative MRI biomarkers to aid them in their evaluation of many neurodegenerative conditions. In the same respect, quantitative measurements of lesion volume and lesion distribution have significant value for clinicians evaluating disease progression associated with T2 FLAIR hyperintensities.
In chronic diseases where disease progression is an important factor in the disease evaluation, accuracy and more importantly reproducibility are especially essential. Evaluations based on clinicians’ visual inspection and manual segmentation are not only time consuming but also often vulnerable to inter- and intra-rater variability, resulting in low reproducibility. To overcome subjective evaluations, objective, automated lesion segmentation tools have been developed, such as the LesionQuant module of NeuroQuant and are now available for clinical practice.
Since the appearance of lesions may vary across different MRI protocols, incorporating multiple MRI studies provides more information to accurately delineate lesions. Additionally, several neurological conditions present with lesions in the brain that show FLAIR hypointensities on MRI and are usually correlated to disease activity. To identify, quantify and visualize lesion volumes, LesionQuant combines T2 FLAIR with 3D T1 scans.
This white paper demonstrates that fully automated LesionQuant based T2 FLAIR lesion segmentation is both accurate and reproducible, by means of several objective segmentation evaluation methods.
To learn more, download the LesionQuant Performance Evaluation white paper, or visit our website to see all of our available white papers.
